git SSH 连接使用代理
前言 🔗
git SSH 连接使用代理。
众所周知, github 在国内属于时能访问,时而gg 。
在 git 官方的配置中,已经支持对 http 和 https 的代理了,这里我们以 V2rayN 为例, V2rayN 默认的 http 代理为 http://localhost:10809 ,然后执行以下脚本:
git config --global http.proxy http://localhost:10809
git config --global https.proxy http://localhost:10809这样子我们使用 git clone https://github.com/Dedicatus546/jm-desktop.git 时就能走代理。
但是这样有一个问题,就是如果我们想要使用 git push 时,每次都得提交账号和密码。
虽然 git 提供了 git config credential.helper store 来避免重复输入账号和密码,但是这会将账号和密码信息明文保存到本地文件上,这对账号的安全存在风险。
所以一般我们是会使用 ssh 的方式来克隆仓库,在本地上生成一个公钥和私钥,然后把公钥设置到 github 上,就可以使用了。
但是 ssh 的方式并不走上面的代理设置。我们需要在 ssh 侧来设置。
正文 🔗
window 上设置代理 🔗
在 window 上,我们需要一个 ncat 命令,来代理 ssh 连接。
为了能够调用 ncat 命令,我们需要去 nmap 官网下载 window 对应的安装包
Download the Free Nmap Security Scanner for Linux/Mac/Windows
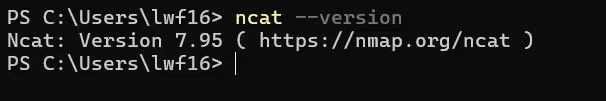
安装之后我们可以测试一下命令
ncat --version效果如下:
接着我们执行 ncat -h ,看看用法:
Ncat 7.95 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Usage: ncat [options] [hostname] [port]
Options taking a time assume seconds. Append 'ms' for milliseconds,
's' for seconds, 'm' for minutes, or 'h' for hours (e.g. 500ms).
-4 Use IPv4 only
-6 Use IPv6 only
-C, --crlf Use CRLF for EOL sequence
-c, --sh-exec <command> Executes the given command via /bin/sh
-e, --exec <command> Executes the given command
--lua-exec <filename> Executes the given Lua script
-g hop1[,hop2,...] Loose source routing hop points (8 max)
-G <n> Loose source routing hop pointer (4, 8, 12, ...)
-m, --max-conns <n> Maximum <n> simultaneous connections
-h, --help Display this help screen
-d, --delay <time> Wait between read/writes
-o, --output <filename> Dump session data to a file
-x, --hex-dump <filename> Dump session data as hex to a file
-i, --idle-timeout <time> Idle read/write timeout
-p, --source-port port Specify source port to use
-s, --source addr Specify source address to use (doesn't affect -l)
-l, --listen Bind and listen for incoming connections
-k, --keep-open Accept multiple connections in listen mode
-n, --nodns Do not resolve hostnames via DNS
-t, --telnet Answer Telnet negotiations
-u, --udp Use UDP instead of default TCP
--sctp Use SCTP instead of default TCP
-v, --verbose Set verbosity level (can be used several times)
-w, --wait <time> Connect timeout
-z Zero-I/O mode, report connection status only
--append-output Append rather than clobber specified output files
--send-only Only send data, ignoring received; quit on EOF
--recv-only Only receive data, never send anything
--no-shutdown Continue half-duplex when receiving EOF on stdin
--allow Allow only given hosts to connect to Ncat
--allowfile A file of hosts allowed to connect to Ncat
--deny Deny given hosts from connecting to Ncat
--denyfile A file of hosts denied from connecting to Ncat
--broker Enable Ncat's connection brokering mode
--chat Start a simple Ncat chat server
--proxy <addr[:port]> Specify address of host to proxy through
--proxy-type <type> Specify proxy type ("http", "socks4", "socks5")
--proxy-auth <auth> Authenticate with HTTP or SOCKS proxy server
--proxy-dns <type> Specify where to resolve proxy destination
--ssl Connect or listen with SSL
--ssl-cert Specify SSL certificate file (PEM) for listening
--ssl-key Specify SSL private key (PEM) for listening
--ssl-verify Verify trust and domain name of certificates
--ssl-trustfile PEM file containing trusted SSL certificates
--ssl-ciphers Cipherlist containing SSL ciphers to use
--ssl-servername Request distinct server name (SNI)
--ssl-alpn ALPN protocol list to use
--version Display Ncat's version information and exit这里面重要的就是 ncat [options] [hostname] [port] 。
其中 [options] 配置中,我们只要知道 --proxy <addr[:port]> 和 --proxy-type <type> 即可,即命令类似:
# 这里以 V2rayN 的默认 socks 地址为例
ncat --proxy localhost:10808 --proxy-type socks5 hostname port接着我们在 .ssh 文件夹下创建一个 config 文件,写入以下内容:
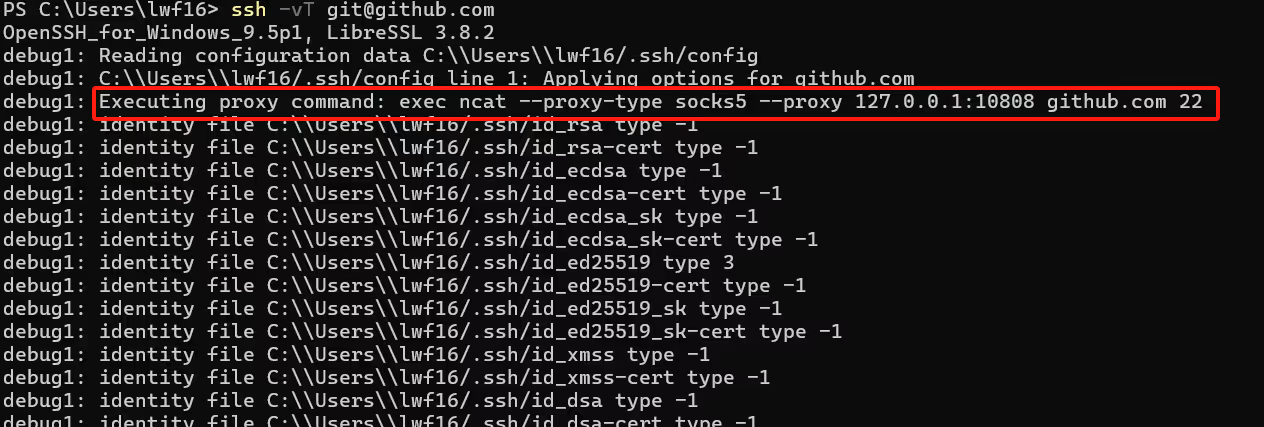
Host github.com
ProxyCommand ncat --proxy-type socks5 --proxy 127.0.0.1:10808 %h %p这个 ProxyCommand 的配置可以在 ProxyCommand - ssh_config 查阅。
这里这个 %h 和 %p 就是该命令提供的 TOKEN ,刚好对应 ncat 命令的后两个参数。
然后打开控制台,执行 ssh -vT [email protected] 之后,可以看到:
如果全部没问题,最后会输出一句:
Hi Dedicatus546(这里是你的密钥对应的用户)! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.现在就可以愉快地克隆项目了,速度超快,超爽。
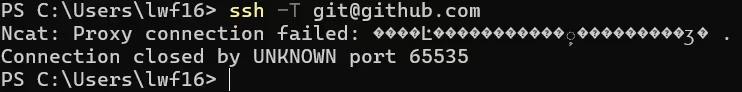
不过需要注意,要确保 V2rayN 启动,不然代理地址不存在的话 ssh 连接会失败:
linux 上设置代理 🔗
linux 上和 window 上其实差不多,可以下载 ncat 的 linux 版本的 rpm 包:
接着同样在 config 文件中配置即可。
linux 下可能存在不同种类的代理命令(比如 nc 命令),只需要根据对应的命令修改 ProxyCommand 即可。